

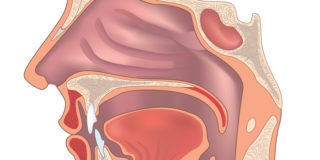
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is cancer that takes place in the nasopharynx. The nasopharynx is situated behind the nose and above the throat. Nasopharyngeal cancer is uncommon in the United States. It is much more common in other regions of the world, especially in Southeast Asia. Nasopharyngeal cancer is hard to identify early. This is likely since the nasopharynx is not easy to examine, and the symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer are similar to other common conditions.
Medication for nasopharyngeal cancer involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both. You may work with your specialist to determine the particular approach for your specific situation.
In the early phases, nasopharyngeal cancer might not cause symptoms. Possible notable symptoms of this condition include the following.
The first symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer might not always trigger you to visit your doctor. See your ENT doctor in Los Angeles if you realize persistent and unusual changes in the body that do not seem accurate to you, for instance, strange nasal congestion.
If you visit your doctor with symptoms that might indicate nasopharyngeal cancer, they will ask about these symptoms and run tests. This might include examining the throat with a light and a small mirror. Your doctor will suggest you visit a specialist (commonly called oncologist) if he thinks more tests are needed. Several tests can be done in the hospital to detect nasopharyngeal cancer and exclude other conditions. Some tests that can be performed include the following:
Physical Test and History
This is a test of the body for general health symptoms, including looking for signs of other diseases or other unusual signs. The doctor will look into the medical history of the person’s health habits and previous treatments and illnesses.
Neurological exam
This is a sequence of tests and questions to check the spinal cord’s function, brain, and nerves. The test checks an individual’s coordination, mental state, ability to pace normally, and how good the senses, muscles, and reflexes function. This might also be referred to as a neurological or neuro exam.
Biopsy
This is the removal of tissues or cells so that a pathologist can view them under a microscope and look for signs of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The tissue section is removed at the time of one of these procedures.
Nasoscopy
This is a procedure to check inside your nose for unusual areas. A rhinoscope is put in via your nose. A rhinoscope refers to a thin tubular instrument with a lens and a light for viewing. It might also have a device to remove the tissue samples, which are examined under a microscope.
Upper Endoscopy
This is a process to look inside the throat, nose, stomach, esophagus, and duodenum. An endoscope is put in through the mouth into the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum. An endoscope refers to a thin tubular instrument with a lens and light for viewing.
MRI
This procedure utilizes radio waves, a magnet, and a computer to create a series of comprehensive images of parts of the body. This technique is also known as NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging).
Computed Tomography (CT) scan
This procedure takes a sequence of detailed images of parts of the body, like the upper abdomen and the chest, from different angles. The photos are taken by a computer connected to an x-ray device. A dye might be injected or swallowed into a vein to assist the tissues or organs in showing up more plainly.
Cancer starts when genetic mutations trigger normal cells to develop uncontrollably, invade adjacent structures, and finally spread to other body regions. In nasopharyngeal cancer, this process starts in the squamous cells, which line the nasopharynx exterior.
The exact cause of the genetic mutations that result in nasopharyngeal cancer is unknown. However, factors like the Epstein-Barr virus have been found to raise the risk of nasopharyngeal cancer. However, it is unclear why other individuals with all potential factors never grow cancer, while others without obvious risk elements.
Researchers have recognized some factors that crop up to increase your possibility of growing nasopharyngeal cancer.
Complications of nasopharyngeal cancer may be:
Most individuals with nasopharyngeal cancer have regional metastases. This means that cancer cells have migrated from the original tumor to nearby areas. Cancer cells that move to other parts of the body (distant metastases) travel to the lungs, bones, and liver.
There is no sure way to prevent nasopharyngeal cancer. However, if you are concerned about nasopharyngeal cancer risk, consider avoiding behaviors related to the disease. For example, you can choose to reduce the number of salty foods you consume or avoid altogether.
The prognosis for nasopharyngeal cancer depends on your general health, age, and how advanced the condition is when it is diagnosed. Radiation therapy can regularly cure a very early-stage of nasopharyngeal cancer; however, the condition is diagnosed at a later stage because it does not cause obvious signs and symptoms until later. More progressive cancers are cured with a mixture of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. They are often treatable if cancer has not spread beyond the neck and head area. To access quality services, search for the following treatments: laryngoscopy, adenoidectomy, or bronchoscopy in Los Angeles.